Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Hua, Y.*; Narumi, Issei; Gao, G.*; Tian, B.*; Sato, Katsuya; Kitayama, Shigeru; Shen, B.*
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 306(2), p.354 - 360, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:152 Percentile:95.76(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We have identified a unique deinococcal gene,  , as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which
, as a general switch for downstream DNA repair and protection pathways, from a natural mutant, in which  is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with
is disrupted by a transposon. Complete functional disruption of the gene in wild-type leads to dramatic sensitivity to ionizing radiation. Radioresistance of the disruptant could be fully restored by complementation with  . In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of
. In response to radiation stress, PprI can significantly and specifically induce the gene expression of  and
and  and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
and enhance the enzyme activities of catalases. These results strongly suggest that PprI plays a crucial role in regulating multiple DNA repair and protection pathways in response to radiation stress.
 -radiation
-radiationYokoya, Akinari; Cunniffe, S. M. T.*; O'Neill, P.*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 124(30), p.8859 - 8866, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:87 Percentile:87.69(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Hisashi
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 19(5), p.839 - 851, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:26.27(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.158 - 171, 2002/03
 is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of
is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of  . The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application
. The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application  and
and  .
.

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.172 - 184, 2002/03
 a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in
a DNA damage response mechanism. However, the damage response is poorly understood in  . By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in
. By investigating the function of deinococcal proteins, we found that, unlike in  , LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in
, LexA is not involved in the regulation of RecA in  . This, in turn, led us to speculate that
. This, in turn, led us to speculate that  has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control
has an alternative DNA damage response mechanism with which to control  expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of
expression. Recently, we discovered that a novel protein regulates the expression of  gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of
gene. The novel regulatory protein (designated as PprI) also control the induction of  gene following
gene following  irradiation. Thus,
irradiation. Thus,  possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
possesses unique mechanisms of DNA damage recognition and repair gene induction.
 is not involved in RecA induction following
is not involved in RecA induction following  irradiation
irradiationNarumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Yanagisawa, Tadashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
Journal of Bacteriology, 183(23), p.6951 - 6956, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:91 Percentile:83.71(Microbiology)The involvement of LexA in induction of RecA was investigated in  . As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following
. As in the wild-type strain, an increase in RecA protein synthesis following  irradiation was detected in a
irradiation was detected in a 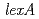 disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in
disruptant, indicating that LexA is not involved in the induction of RecA in  .
.
Pinak, M.
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.30 - 39, 2001/00
no abstracts in English